Table of Contents
What is iPaaS (integration-Platform-as-a-Service)?
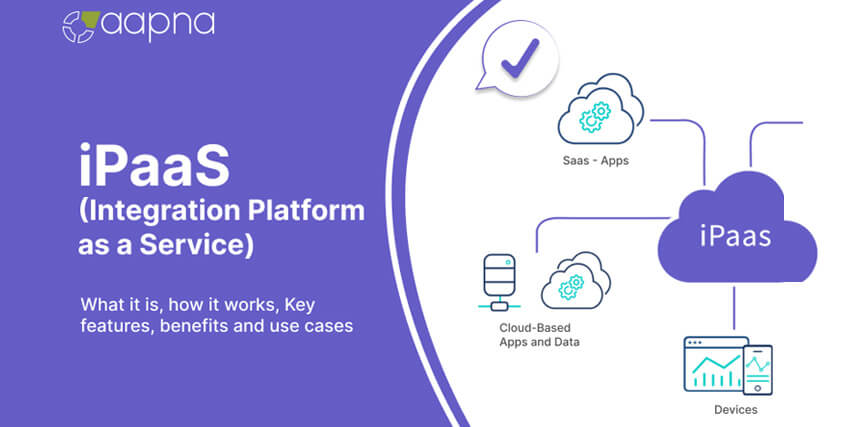
iPaaS stands for Integration Platform as a Service. It is a cloud-based platform that facilitates the integration of various applications, systems, and data sources within your organization. iPaaS allows you to connect different software applications, databases, and systems together, enabling seamless data exchange and workflow automation.
Key Features of iPaaS Include:
- Integration: iPaaS provides pre-built connectors and APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) to connect different applications and systems, both on-premises and in the cloud. It enables the exchange of data, messages, and events between these systems.
- Data Transformation: iPaaS allows for data mapping and transformation between different formats and structures, ensuring compatibility and consistency across integrated systems. It simplifies the process of converting data from one system’s format to another.
- Workflow Automation: iPaaS platforms often include visual development tools and workflow engines that enable the creation of automated business processes. This automation improves efficiency and reduces manual effort by automating repetitive tasks and streamlining data flows.
- Scalability and Flexibility: iPaaS solutions are designed to scale as per the organization’s needs. They can handle a large volume of data and transactions, supporting businesses as they grow and expand. iPaaS also offers flexibility in terms of adding or removing integrations based on changing business requirements.
- Monitoring and Management: iPaaS provides monitoring capabilities to track data flows, identify issues, and ensure smooth operations. It offers dashboards, alerts, and logging functionalities to monitor integration performance and troubleshoot any problems that arise.
- Security and Governance: iPaaS platforms typically include security features such as data encryption, access controls, and identity management to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of integrated data. They also provide governance capabilities to enforce policies and compliance requirements.
The Enterprise Integration Challenge
The enterprise integration challenge refers to the difficulties and complexities faced by organizations when trying to connect and integrate various systems, applications, and data across their entire enterprise. It is a common issue that arises due to the growing number of disparate technologies, legacy systems, and diverse data formats used within an organization.
Some Key Aspects of the Enterprise Integration Challenge Include:
- System Heterogeneity: Organizations often use a mix of different systems, such as ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), CRM (Customer Relationship Management), HRM (Human Resource Management), and more. These systems may be built on different technologies, have varying data formats, and operate with different protocols, making integration a complex task.
- Data Inconsistency: Data resides in different systems and databases across an organization. Maintaining consistency and accuracy of data as it flows between systems can be challenging, as data may have different structures, definitions, and quality standards. Ensuring data integrity and synchronization becomes crucial for effective integration.
- Legacy Systems: Many organizations still rely on legacy systems that were developed years ago. These systems may lack modern integration capabilities, use outdated technologies, or have limited support for standard integration protocols. Integrating these legacy systems with newer technologies can be time-consuming and complex.
- Scalability and Performance: As organizations grow and expand, the volume of data and transactions also increases. Integrations need to be scalable to handle the growing data flows and ensure optimal performance. Scaling integrations while maintaining data consistency and without disrupting existing processes is a significant challenge.
- Security and Compliance: Integration involves the exchange of data between different systems, which raises concerns about data security and compliance with regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation). Protecting sensitive data during integration and ensuring compliance with data protection laws becomes a critical consideration.
- Collaboration and Communication: Integration often requires collaboration between different teams and departments within an organization. Effective communication and coordination among teams responsible for different systems and applications are essential to ensure successful integration projects.
To overcome the enterprise integration challenge, organizations often turn to integration platforms and technologies, such as iPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service) solutions. These platforms provide pre-built connectors, data transformation capabilities, workflow automation, and monitoring tools to simplify integration processes. Additionally, adopting integration best practices, utilizing standardized protocols and APIs, and having a well-defined integration strategy can help organizations navigate the complexities of enterprise integration and achieve seamless connectivity across their systems and data sources.
How iPaaS Works
iPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service) works by providing a cloud-based platform that facilitates the integration of different systems, applications, and data within an organization. Here’s a general overview of how iPaaS works:
- Cloud-Based Infrastructure: iPaaS operates on a cloud-based infrastructure, which means the platform and its services are hosted and managed by a third-party provider. This eliminates the need for organizations to set up and maintain their own hardware or software infrastructure.
- Pre-Built Connectors: iPaaS offers a wide range of pre-built connectors or adapters that allow for easy integration with your various systems, applications, and data sources. These connectors are designed to connect to popular enterprise software, databases, APIs, and protocols.
- Data Mapping and Transformation: iPaaS enables you to map and transform data between different systems or formats. It provides tools and interfaces that allow you to define mappings, specify data transformations, and ensure compatibility between connected systems. This ensures seamless data flow and consistency across integrated applications.
- Workflow Automation: iPaaS platforms often include visual development tools or low-code/no-code environments that enable users to create and automate workflows or business processes. Users can define triggers, actions, and conditions to orchestrate data flows and automate tasks across connected systems.
- Monitoring and Management: iPaaS provides monitoring capabilities to track the performance and health of integrations. It offers dashboards, logs, and alerts that enable users to monitor data flows, identify bottlenecks or errors, and take proactive measures to ensure smooth operations. It also allows users to manage integrations, configure settings, and make adjustments as needed.
- Security and Governance:iPaaS platforms prioritize security and offer features such as data encryption, access controls, and identity management to protect the integrity and confidentiality of integrated data. They also provide governance capabilities to enforce policies, compliance requirements, and data privacy regulations.
- Scalability and Flexibility: iPaaS platforms are designed to handle a large volume of data and transactions, and they can scale as the organization’s needs grow. They offer flexibility in terms of adding or removing integrations, adjusting workflows, and accommodating changing business requirements.
Overall, iPaaS simplifies the complexity of integration by providing a unified platform that enables seamless data exchange, workflow automation, and connectivity between different systems. It empowers organizations to streamline their processes, improve data visibility, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
Benefits of iPaaS
iPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service) offers several benefits to organizations looking to streamline their integration processes and connect various systems and applications. Some key benefits of iPaaS include:
- Simplified Integration: iPaaS provides a centralized platform for integration, making it easier to connect disparate systems, applications, and data sources. It eliminates the need for custom-coded integrations and complex point-to-point connections, simplifying the integration process.
- Time and Cost Savings:With pre-built connectors and visual development tools, iPaaS significantly reduces the time and effort required for integration projects. It eliminates the need for extensive coding and development, allowing organizations to implement integrations more quickly and cost-effectively.
- Scalability and Flexibility: iPaaS platforms are designed to handle a large volume of data and transactions, allowing organizations to scale their integrations as needed. They provide flexibility in adding or removing integrations, adjusting workflows, and accommodating changing business requirements.
- Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity: By automating workflows and data exchange, iPaaS improves overall operational efficiency. It eliminates manual data entry, reduces errors, and streamlines business processes, leading to increased productivity and time savings for employees.
- Improved Data Visibility and Accuracy: iPaaS enables seamless data integration and synchronization across systems, ensuring data consistency and accuracy. It provides a unified view of data, making it easier to access, analyze, and utilize information from different sources.
- Collaboration and Agility: iPaaS facilitates collaboration between teams and departments within an organization. It enables cross-functional data sharing, supports collaboration on integration projects, and promotes agility by allowing quick changes and adjustments to integrations.
- Security and Compliance: iPaaS platforms prioritize data security and offer robust security features such as encryption, access controls, and identity management. They help organizations meet data privacy and compliance requirements, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS.
- Rapid Adoption of Cloud Technologies: iPaaS is typically cloud-based, making it an ideal solution for organizations adopting cloud technologies. It enables seamless integration between on-premises systems and cloud applications, supporting hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
- Innovation and Future-Proofing: iPaaS allows organizations to leverage emerging technologies and integrate with new applications and systems as they evolve. It enables the adoption of APIs, IoT (Internet of Things), AI (Artificial Intelligence), and other innovative technologies, future-proofing integration capabilities.
- Focus on Core Competencies:By offloading integration complexity to the iPaaS platform, organizations can focus on their core competencies and strategic initiatives. It frees up resources and allows IT teams to concentrate on value-added activities rather than spending time on integration maintenance.
Overall, iPaaS offers organizations a streamlined, cost-effective, and flexible solution for integrating systems, applications, and data. It empowers businesses to optimize their processes, improve productivity, and drive digital transformation initiatives.
iPaaS Use Cases
- Healthcare:iPaaS can be used in healthcare to integrate electronic health record (EHR) systems, patient management systems, billing systems, and other healthcare applications. It enables secure and seamless data exchange between healthcare providers, insurance companies, and patients, facilitating better patient care coordination, claims processing, and compliance with healthcare regulations.
- Retail and E-commerce:In the retail industry, iPaaS can integrate e-commerce platforms, point-of-sale (POS) systems, inventory management systems, and customer relationship management (CRM) tools. It enables real-time inventory updates, order management, customer data synchronization, and seamless integration with payment gateways and shipping providers.
- Manufacturing: iPaaS can connect manufacturing systems, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP), manufacturing execution systems (MES), supply chain management (SCM), and quality management systems (QMS). It enables end-to-end visibility across the manufacturing value chain, streamlines production planning and scheduling, and supports efficient inventory management and supply chain integration.
- Financial Services: In the financial industry, iPaaS can integrate core banking systems, payment gateways, risk management systems, customer relationship management (CRM), and regulatory reporting systems. It facilitates secure data exchange, supports real-time payment processing, enables compliance with financial regulations, and improves customer onboarding and service delivery.
- Hospitality and Travel: iPaaS can integrate hotel reservation systems, property management systems (PMS), customer loyalty systems, and online travel platforms. It enables seamless bookings, real-time availability updates, customer data synchronization, and integration with third-party travel service providers, enhancing the guest experience and improving operational efficiency.
- Logistics and Transportation: In the logistics and transportation industry, iPaaS can integrate transportation management systems (TMS), warehouse management systems (WMS), fleet management systems, and order management systems. It enables real-time tracking and visibility of shipments, optimizes route planning and scheduling, automates order fulfillment processes, and integrates with logistics partners for efficient supply chain management.
- Education: iPaaS can integrate learning management systems (LMS), student information systems (SIS), content management systems, and communication platforms used in educational institutions. It enables seamless student data management, supports online learning and collaboration, facilitates course enrollment and grading processes, and enhances communication between students, teachers, and administrators.
- Telecommunications:In the telecommunications industry, iPaaS can integrate customer relationship management (CRM) systems, billing systems, network management systems, and self-service portals. It enables streamlined customer onboarding and support processes, facilitates accurate billing and revenue management, and integrates with network monitoring systems for proactive issue resolution.
These are just a few examples of how iPaaS can be applied in specific industries. iPaaS provides the flexibility and customization necessary to address industry-specific integration challenges and optimize business processes within each sector.